Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab
- Tae Hyun Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Yu Ri Cho, Young-Hwan Koh, Joong-Won Park
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(2):330-340. Published online May 16, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.04.14
- 1,802 Views
- 112 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
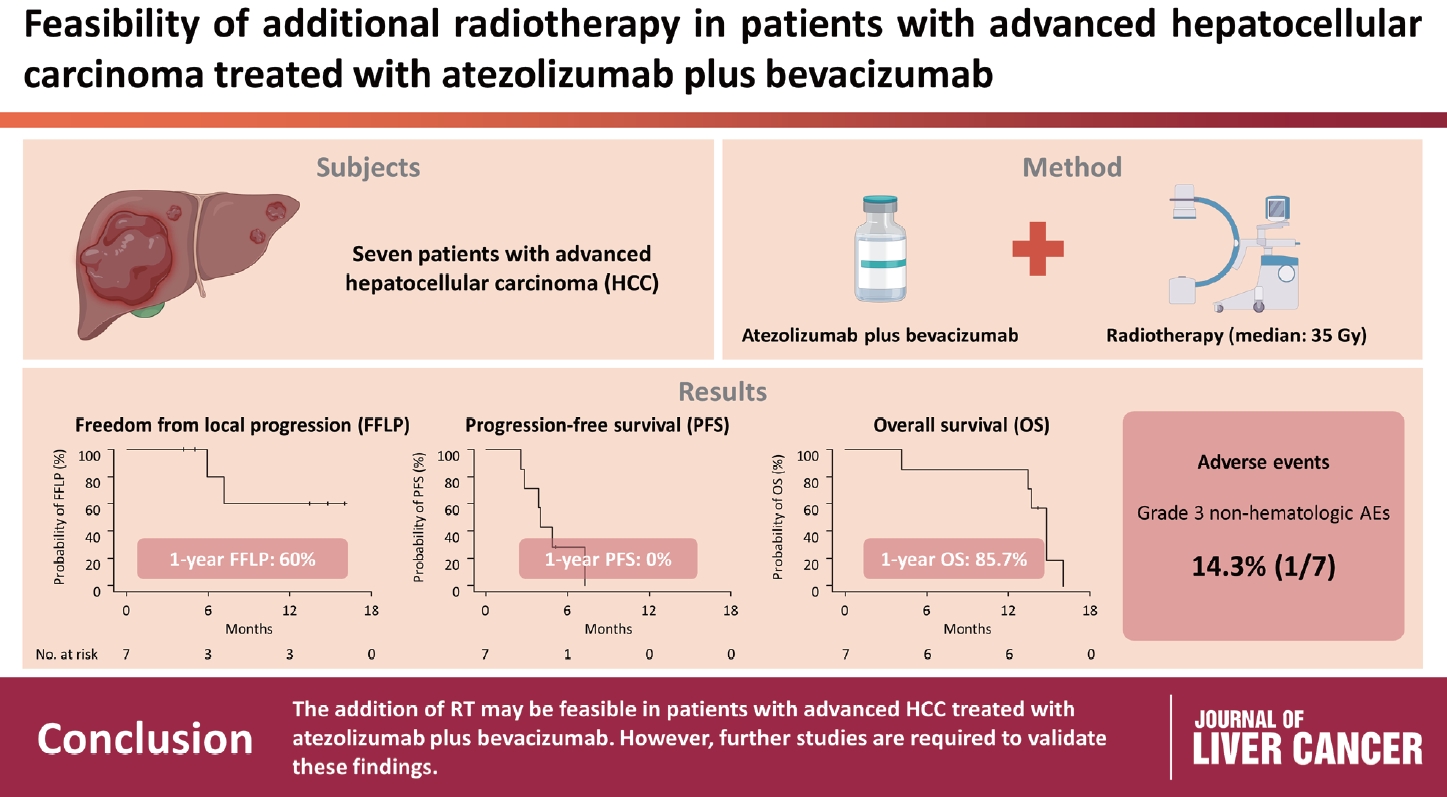
Radiotherapy (RT) is an effective local treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, whether additional RT is safe and effective in patients with advanced HCC receiving atezolizumab plus bevacizumab remains unclear. This retrospective cohort study aimed to evaluate the feasibility of additional RT in these patients.
Methods
Between March and October 2021, we retrospectively analyzed seven patients with advanced HCC who received RT during treatment with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab. The median prescribed RT dose was 35 Gy (range, 33–66). Freedom from local progression (FFLP), progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS) after RT were analyzed.
Results
The median follow-up duration after RT was 14.2 months (range, 10.0–18.6). Of the seven patients, disease progression was noted in six (85.7%), the sites of disease progression were local in two (28.6%), intrahepatic in four (57.1%), and extrahepatic in four (57.1%). The median time of FFLP was not reached, and PFS and OS times were 4.0 (95% confidence interval [CI], 3.6–4.5) and 14.8% (95% CI, 12.5–17.2) months, respectively. The 1-year FFLP, PFS, and OS rates were 60% (95% CI, 43.8–76.2), 0%, and 85.7% (95% CI, 75.9–95.5), respectively. Grade 3 or higher hematologic adverse events (AEs) were not observed, but grade 3 nonhematologic AEs unrelated to RT were observed in one patient.
Conclusions
The addition of RT may be feasible in patients with advanced HCC treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab. However, further studies are required to validate these findings. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Letter regarding “Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab”
Sun Hyun Bae, Hee Chul Park
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 402. CrossRef
- Letter regarding “Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab”

Case Reports
- A case of successful surgical treatment for peritoneal seeding of hepatocellular carcinoma after radiotherapy and atezolizumab plus bevacizumab combination treatment
- Yuri Cho, Bo Hyun Kim, Tae Hyun Kim, Young Hwan Koh, Joong-Won Park
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(1):206-212. Published online February 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.02.09
- 1,473 Views
- 58 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
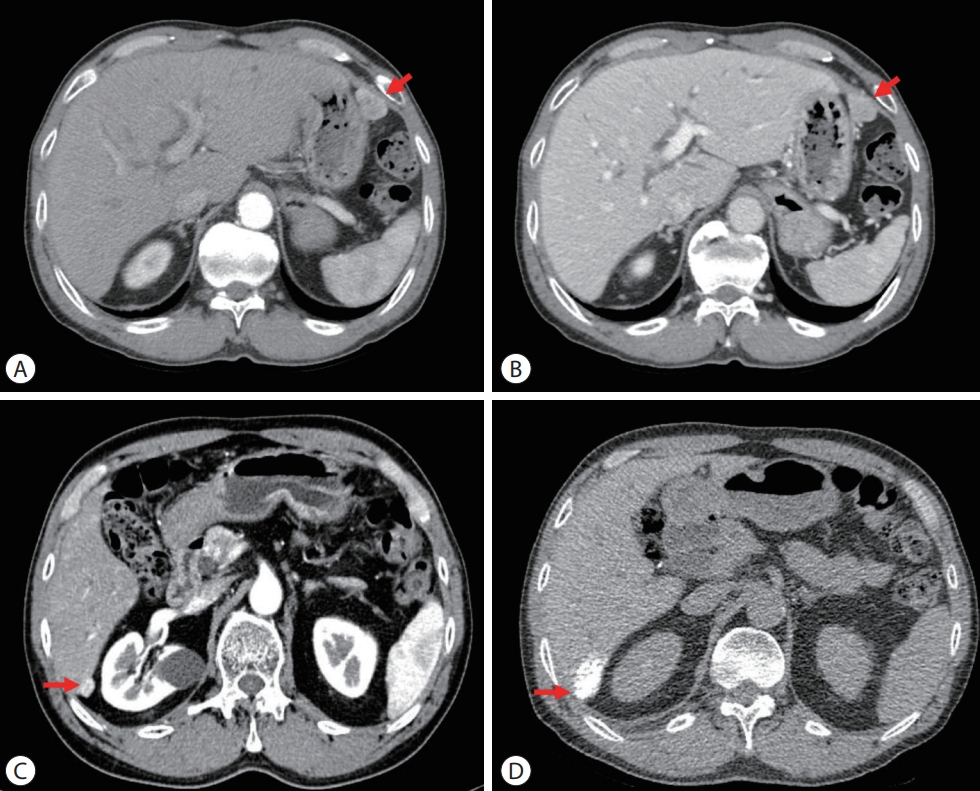
PDF - Peritoneal seeding of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is incurable and has poor prognosis. A 68-year-old man underwent surgical resection for a 3.5 cm single nodular HCC at the tip of segment 3 and transarterial chemoembolization for a 1.5 cm-sized recurrent HCC at the tip of segment 6. 3 months later, an increasing 1 cm pelvic nodule on the rectovesical pouch warranted radiotherapy. Although it stabilized, a new 2.7 cm-sized peritoneal nodule in the right upper quadrant (RUQ) omentum appeared 3.5 years after radiotherapy. Hence, omental mass and small bowel mesentery mass excision were performed. 3 years later, recurrent peritoneal metastases in the RUQ omentum and rectovesical pouch progressed. 33 cycles of atezolizumab and bevacizumab treatment elicited stable disease response. Finally, laparoscopic left pelvic peritonectomy was performed without tumor recurrence. Herein, we present a case of HCC with peritoneal seeding that was successfully treated with surgery after radiotherapy and systemic therapy, leading to complete remission.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab
Tae Hyun Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Yu Ri Cho, Young-Hwan Koh, Joong-Won Park
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 330. CrossRef
- Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab

- Sorafenib combined with radiation therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal and hepatic vein invasion extending to the inferior vena cava: a complete response case according to modified RECIST criteria
- Yuri Cho, Bo Hyun Kim, Tae Hyun Kim, Young Hwan Koh, Joong-Won Park
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(1):63-68. Published online February 14, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.01.18

- 2,776 Views
- 90 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The prognosis of patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with tumor thrombus extending to the inferior vena cava (IVC) is extremely poor. Herein, we present a rare case of advanced HCC that was treated with sorafenib and radiotherapy, leading to complete remission. This patient had a 9 cm infiltrative HCC occupying almost the entire left lobe with a tumor thrombus extending through the hepatic vein, IVC, and left portal vein. The patient received 400 mg sorafenib twice daily. One year after the start of sorafenib, intensity-modulated radiation therapy for viable HCC and tumor thrombus was performed with a dose of 5,500 cGy. Twenty-seven months after the starting date of sorafenib, there was no intratumoral arterial enhancement, which suggested a complete response according to the modified RECIST criteria. This case suggests that the combination of sorafenib and radiotherapy might provide clinical benefits in patients with advanced HCC with IVC tumor thrombus.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab
Tae Hyun Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Yu Ri Cho, Young-Hwan Koh, Joong-Won Park
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 330. CrossRef - Is multidisciplinary treatment effective for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus?
Won Hyeok Choe
Journal of Liver Cancer.2022; 22(1): 1. CrossRef
- Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab

Review Article
- Systemic therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: consideration for selecting second-line treatment
- Bo Hyun Kim, Joong-Won Park
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(2):124-138. Published online September 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2021.09.23
- 3,994 Views
- 112 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
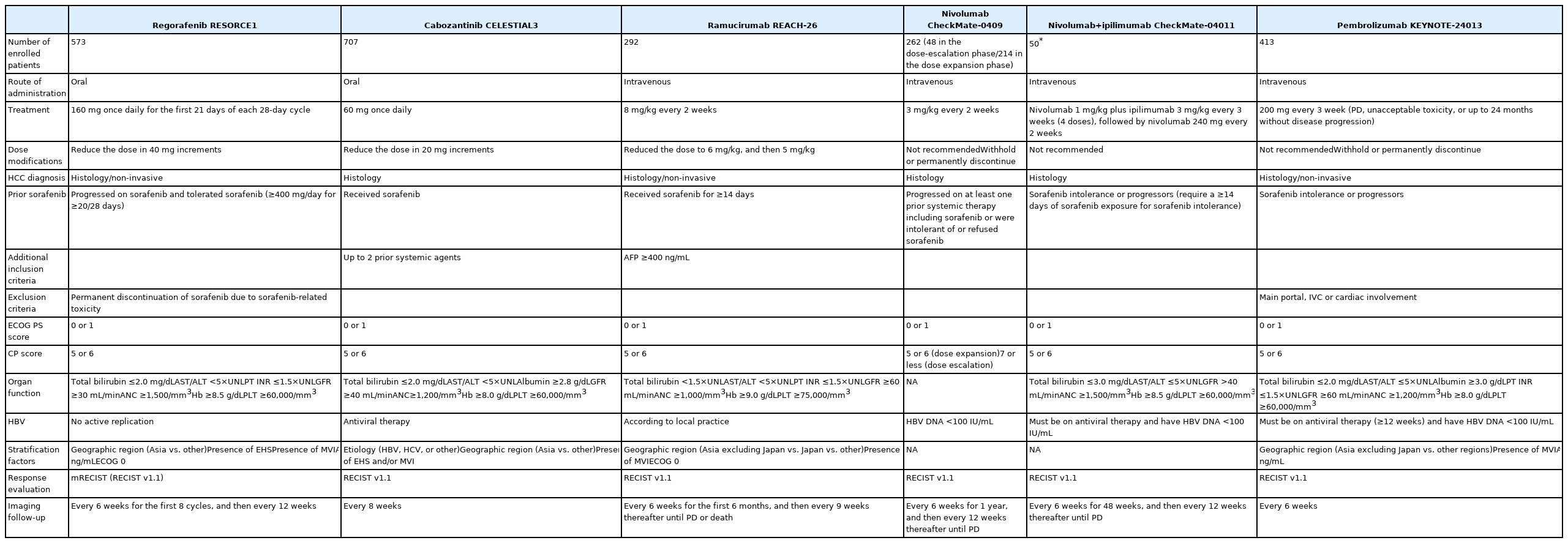
PDF - Several molecular-targeted agents have been tested as first- or second-line therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) but failed to improve clinical outcomes; sorafenib has been the only approved systemic agent for treating HCC for almost 10 years. Regorafenib resulted in a significant improvement in overall survival and thus was approved for HCC patients previously treated with sorafenib. Subsequently, cabozantinib and ramucirumab demonstrated superior overall survival compared with placebos in phase III clinical trials. Immune checkpoint inhibitors such as nivolumab with or without ipilimumab and pembrolizumab are also available in some countries for patients who are unresponsive to sorafenib. Some second-line agents are available for patients who are unresponsive to sorafenib; however, little is known about the considerations for selecting appropriate secondline systemic agents. Hence, this study aimed to review the current and future perspectives of second-line systemic agents.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Expression of Peptidyl Arginine Deiminase 2 Is Closely Associated with Recurrence in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Sunho Uhm, Yoon Cho, Ji-Young Choe, Ji Park, Min-Jeong Kim, Won-Ho Han, Junyong Lee, Jung Lee, Dong Shin, Jae Soh, Hyun Lim, Ho Kang, Sung-Hoon Moon, Sung-Eun Kim
Diagnostics.2023; 13(4): 659. CrossRef - Expert consensus on the management of adverse events in patients receiving lenvatinib for hepatocellular carcinoma
Bo Hyun Kim, Su Jong Yu, Wonseok Kang, Sung Bum Cho, Soo Young Park, Seung Up Kim, Do Young Kim
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2022; 37(3): 428. CrossRef
- Expression of Peptidyl Arginine Deiminase 2 Is Closely Associated with Recurrence in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma

Case Report
- Ruptured Massive Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cured by Transarterial Chemoembolization
- Ji Eun Lee, Joong-Won Park, In Joon Lee, Bo Hyun Kim, Seoung Hoon Kim, Hyun Beom Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(2):154-159. Published online September 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.2.154
- 2,913 Views
- 62 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
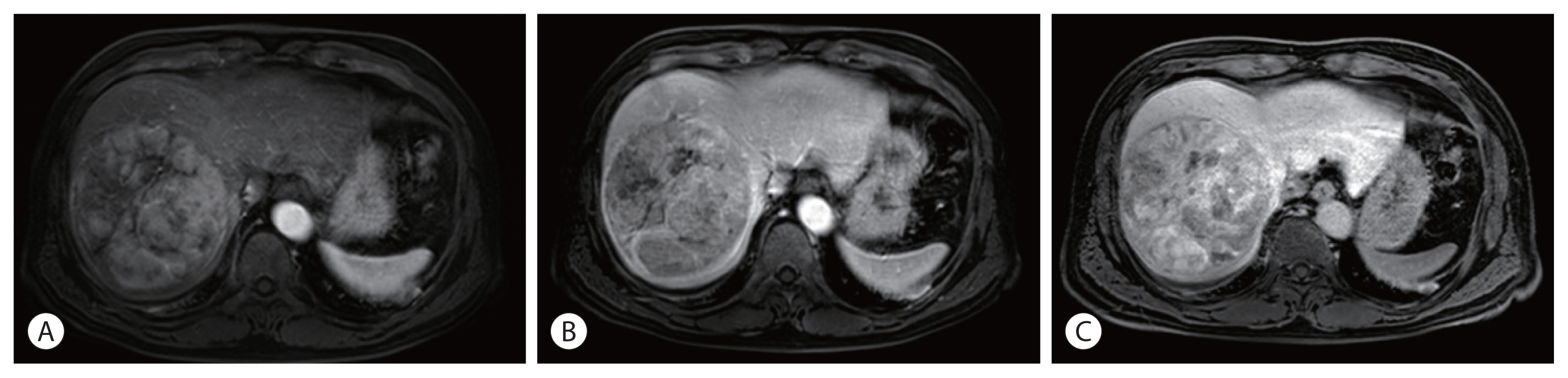
PDF - Spontaneous tumor rupture is a serious but rare complication of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and has a low survival rate. Here, we report a case of massive HCC that ruptured and was treated successfully with transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). A 55-year-old man with abdominal pain was diagnosed with a 12-cm-wide ruptured HCC at segment 8. The overall liver function was scored as Child–Pugh A, but the single nodule tumor had ruptured; therefore, TACE treatment was initiated. After the first TACE treatment, residual tumors were found; thus, secondary TACE was performed 5 months later. No new lesions or extrahepatic metastases were found 16 months after the first TACE treatment, so hepatic resection was performed for curative treatment. The postoperative pathology results did not reveal any cancer cells; hence, TACE alone resulted in a cure. We report this case because the cure has been maintained for more than 3 years after resection.

Review Article
- New Targeted Agents for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Joong-Won Park
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2008;8(1):16-17. Published online June 30, 2008
- 484 Views
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Most patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) present with advanced stage tumors at the time of initial diagnosis, only about 30%, who present with early stage tumors, undergo radical therapies such as resection, liver transplantation, and percutaneous ablation. Thus, over 50% of HCC patients receive palliative treatments. The newly developed, molecularly targeted agents, sorafenib is the first agent that has shown significant survival benefits for European and American patients with advanced HCC and sets the new standard for the first-line treatment of these patients. The role of sorafenib and other promising agents should be examined in the adjuvant setting after RFA, TACE, surgical resection or selective settings in liver transplantation in an attempt to improve further the outcomes of these patients.

Case Reports
- Extrahepatic Bile Duct Hepatocellular Carcinoma Presenting as Obstructive Jaundice
- Ju Hyun Shim, Joong-Won Park, Sung-Sik Han, Joon-Il Choi, Seong Hoon Kim, Sang Jae Park, Eun Kyung Hong, Chang-Min Kim
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2008;8(1):51-54. Published online June 30, 2008
- 529 Views
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Obstructive jaundice is a rare initial symptom of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients. We herein report a patient with extrahepatic bile duct HCC mimicking common bile duct (CBD) cancer. A 55-year-old woman with no risk factors developed jaundice of the obstructive type. On dynamic computed tomography, a low attenuated mass located in the lumen of CBD with the invasion of right posterior hepatic parenchyma was identified. After percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage, we performed hepatectomy. Pathologic examination of the lesion confirmed the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma with biliary cell differentiation extended in the CBD.

- Successful Resection of Modified UICC stage Ⅳa Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Arterial Chemoembolization & Radiation Therapy: A Case Report
- Min An, Joong-Won Park, Jung A Shin, Tae Hyun Kim, Seong-Hoon Kim, Sang-Jae Park, Woo Jin Lee, Eun Kyung Hong, Chang-Min Kim
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2006;6(1):56-59. Published online June 30, 2006
- 569 Views
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Surgical resection is not candidate for advanced stage hepatocellular cacinoma with portal vein thrombosis, but transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) or radiotherapy can be considered as palliative treatment option. We experienced a 44-old-male who has stage Ⅳa hepatocellular carcinoma. We performed TACE and 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein thrombosis. Because follow up image study showed no viable tumor, we then performed surgical resection. Surgical specimen also showed complete tumor necrosis.

- Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Arterioportal Shunt after Percutaneous Needle Biopsy
- Sang-Hyung Cho, Jae-Hee Cheon, Hong-Suk Park, Seong-Hoon Kim, Sang-Jae Park, Woo-Jin Lee, Eun-Kyung Hong, Joong-Won Park, Chang-Min Kim
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2004;4(1):20-23. Published online June 30, 2004
- 534 Views
- 3 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 51-year-old male was referred to our hospital for further evaluation and treatment of a liver mass. He was a heavy alcoholic. Laboratory findings revealed that anti-HCV was positive, and AFP is below 400 ng/mL. We performed CT scan that showed multiple nodules in the right lobe. Among them, the nodule in the segment Ⅷ showed incomplete enhancement at the arterial phase. Hence, we performed percutaneous needle biopsy for this nodule, and pathologically proved to hepatocellular carcinoma of Edmonson-Steiner grade Ⅱ/Ⅳ. We performed transcatheter arterial chemoembolization(TACE) for multiple hepatocellular carcinomas. Angiography showed nodular tumor staining and arterioportal shunt and arteriovenous shunts at the biopsy site in the segment Ⅷ. We occluded the shunts by using Lipiodol and gelform mixtures and then performed TACE. After TACE, angiography did not show either residual tumor staining or arterioportal and arteriovenous shunts.

- A Resected Case of Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Sang-Jae Park, Joong-Won Park, Seong-Hun Kim, Soon-Ae Lee, Young-Hun Kim, Eun-Kyoung Hong, Chang-Min Kim
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2004;4(1):33-38. Published online June 30, 2004
- 489 Views
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 35 year-old male patient admitted due to epigastric pain for 1 month. He was heavy drinker and spider angioma was obserbed in physical examination. HBsAb, anti-HBs Ab and anti-HCV Ab were all negative and AFP level was normal. AST/ALT were elevated to 178 IU/L and 107 IU/L, respectively. At ultrasonography, CT and MRI, a 2 cm, hypervascular mass was detected in the segment Ⅵ. Segmentectomy of the segment Ⅵ was performed. Tumor size 1.7 cm in maximum diameter and the Edmondson and Steiners grade Ⅰ. High-grade dysplasia was present in the periphery of hepatocellular carcinoma (nodule-in-nodule). Microvascular invasion was not observed and background liver was cirrhotic. He was discharged 10 days after operation without any problem and there has been no evidence of recurrence for the 2 years postoperatively.

- A Case of Early Recurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Curative Hepatic Resection
- Sang-Hyung Cho, Jae-Hee Cheon, Hong-Suk Park, Seong-Hoon Kim, Sang-Jae Park, Woo-Jin Lee, Eun-Kyung Hong, Joong-Won Park, Chang-Min Kim
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2004;4(1):55-58. Published online June 30, 2004
- 484 Views
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 52-year-old male was referred to our hospital for further evaluation and treatment of known hepatocelluar carcinoma. He did not have risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma, such as hepatitis virus infection, alcohol abuse and occupational history. We performed CT scan that showed a single nodule with a diameter of 4 cm in the segment Ⅴ. MR imaging showed the same nodule in the segment Ⅴ without any additional nodule in the liver. We performed segmentectomy for the segment Ⅴ, Ⅵ, and Ⅶ. Five months later, follow-up CT scan showed disseminated hypervascular nodules involving the remaining liver. Hepatic angiography also showed multiple hypervascular nodules in the remaining liver, indicating early recurrence by intrahepatic metastasis. We then performed transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE). At present, this patient underwent TACE for ten times, but was still found to have new intrahepatic metastases, tumor invasion to the portal vein and lymph node metastasis in the peripancreatic area.

- A Case of High Grade Dysplastic Nodule, Diagnosed as Hepatocelluar Carcinoma before Operation
- Sang-Hyung Cho, Joong-Won Park, Hyun-Bae Son, Seong-Hoon Kim, Hyun-Jung Jang, Hong-Suk Park, Woo-Jin Lee, Sang-Jae Park, Eun-Kyung Hong, Chang-Min Kim
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2003;3(1):57-60. Published online July 31, 2003
- 510 Views
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 58-years-old male was referred to our hospital for further evaluation and treatment due to hepatic mass which was found on US. He was a heavy drinker and there was no evidence of abnormal finding in liver function test including HBs Ag and Anti-HCV Ab negative. Liver CT revealed an enhancing hepatic mass on arterial phase. we had confirmed hepatocellular carcinoma by sono-guided liver biopsy, and so performed left lobectomy. After operation, We diagnosed the resected liver specimen not hepatocellular carcinoma but high grade dysplastic nodule by several immunohistochemical staining. There was no evidence of recurrence during 5-month follow-up.

- A Case of Atypical Imaging Finding for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Sang-Hyung Cho, Seong-Hoon Kim, Hyun-Jung Jang, Hong-Suk Park, Woo-Jin Lee, Sang-Jae Park, Joong-Won Park, Eun-Kyung Hong, Chang-Min Kim
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2003;3(1):77-79. Published online July 31, 2003
- 581 Views
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 62-year-old male was referred to our hospital for further evaluation and treatment due to hepatocellular carcinoma. He was performed to TACE once. Threre was no evidence of abnormal finding except HBs Ag positive. We performed four times of TACE. Another hepatic mass was found on Liver CT which was observed in delyed phase not in arterial phase, portal phase. We diagnosed hepatocellular carcinoma by sono-guided Liver biopsy and radiofrequency ablation was performed because of no response to further TACE. There wad no evidence of recurring during 3-month follow-up.

Review Article
- Systemic Treatment of Advanced or Metastatic Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Joong-Won Park, Hark Kyun Kim
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2002;2(1):1-7. Published online July 31, 2002
- 536 Views
- 5 Downloads

Case Report
- A Case of Mixed Hepatocellular and Cholangiocarcinoma
- Jae Hyuk Do, Joong-Won Park, Hyung Joon Kim, Eon Seob Park, Jong Beom Lee, Byung Chul Yoo, Sill Moo Park
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2002;2(1):83-87. Published online July 31, 2002
- 493 Views
- 3 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Mixed hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma (HCC-CC) is an uncommon form of primary liver cancer. Definition of HCC-CC is both hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma in the same tumor or in the same liver. We had experienced a case of HCC-CC. A 49 year-old male, who had social drinking history, admitted due to abdominal distension for about 4 days. Physical findings revealed that he had jaundice and ascites. The serum level of total bilirubin, direct bilirubin, AST, ALT, ALP and LDH were elevated. And serum levels of AFP and CEA were normal. But CA 19-9 level was elevated. Hepatitis B surface antibody was positive and anti-HCV antibody was negative. The level of SAAG was 1.4. The US and CT scans revealed heterogeneous echoic and hypodense multifocal mass like lesions were noted on the S6, S7, S8 and S5. And about 3 cm-sized hperechoic ovoid mass lesion was detected at S6. This lesions was not enhanced after contrast injection in CT scan. The IVC and hepatic veins were stenotic and right portal vein was obstructed due to thrombosis. But main portal vein, left portal vein and hepatic arteries were intact. We performed US guide gun biopsy at this mass-like lesion in S6 and diagnosed as mixed hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma.


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter